一、GStreamer
二、gst-launch
三、在linux环境使用ip-camera
四、在ros环境使用ip-camera
GStreamer是个建立音视频管道的工具包,例如stream一个媒体文件到互联网,再例如把一个test.avi文件stream到一个V4L的camera。V4L的capture主要是用:
1–gst-launch-1.0 for capturing video
2–FFMpeg for saving and editing video
3–v4l-ctl for controlling your video card
4–mpv for viewing videos
5–gst-inspect for listing elements
操作GStreamer主要用gst-launch这个CLI,这个命令行工具可以创建pipeline、初始化、然后运行,例如可以把一个avi媒体文件模拟成摄像头,把ip-camera回环成一个usb-camera,等等。
1–例如最简单的:
$ gst-launch-1.0 fakesrc ! fakesink
这样建立了一条simplest pipline,实现connects a single (fake) source to a single (fake) sink。
2–例如记录视频,create an AVI file with raw video and no audio:
$ gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=$VIDEO_DEVICE ! $VIDEO_CAPABILITIES ! avimux ! filesink location=test.avi
3–例如记录音频,create an AVI file with raw audio and no video:
$ gst-launch-1.0 $alsasrc device=$AUDIO_DEVICE ! $AUDIO_CAPABILITIES ! avimux ! filesink location=test.avi
4–记录音频和视频:
$ gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=$VIDEO_DEVICE ! $VIDEO_CAPABILITIES ! mux. alsasrc device=$AUDIO_DEVICE ! $AUDIO_CAPABILITIES ! mux. avimux name=mux ! filesink location=test-$.avi
This pipe has three parts:a video source leading to a named element (! name. with a full stop means “pipe to the name element”) an audio source leading to the same element a named muxer element leading to a file sink
5–把一个source分为多个out:
$ gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=$VIDEO_DEVICE ! $VIDEO_CAPABILITIES ! avimux ! tee name=network ! filesink location=test.avi tcpclientsink host=127.0.0.1 port=5678
This sends your stream to a file (filesink) and out over the network (tcpclientsink). To make this work, you’ll need another program listening on the specified port (e.g. nc -l 127.0.0.1 -p 5678).
6–从相机查看图片:
$ gst-launch-0.10 v4l2src do-timestamp=true device=$VIDEO_DEVICE ! video/x-raw-yuv,format=(fourcc)UYVY,width=320,height=240 ! ffmpegcolorspace ! autovideosink
7–其它选项
gst-launch -v –gst-debug-level=3,输出的调试信息会多一些。
IP camera, gstreamer and virtual video devices,指明画幅参数。
1、安装
1.1、包
$ sudo apt-get install v4l2loopback-dkms
1.2、源码
如果失败apt-get method may fail durning install. some wranings were treated as errors. Not sure if it’s a compiler compatibility issue.
$ sudo su
$ git clone https://github.com/umlaeute/v4l2loopback.git
$ cd v4l2loopback
$ make && make install
(是否需要sudo忘记了)
2、加载模块
2.1、加载
$ sudo modprobe v4l2loopback
2.2、如果提示not found
$ sudo depmod v4l2loopback
$ sudo modprobe v4l2loopback
2.3、如果还失败
$ sudo apt-get install linux-generic<——–maybe freeze you kernel
$ sudo apt-get install v4l2loopback-dkms
$ sudo depmod v4l2loopback
$ sudo modprobe v4l2loopback<——————
or
$ sudo modprobe v4l2loopback video_nr=7 3、验证
$ v4l2-ctl –list-devices
会出来虚拟设备,这里是video1,我原有的usb-camera是video0是。
Dummy video device (0x0000) (platform:v4l2loopback-000):
/dev/video*
同样也可以
$ dmesg v4l2loopback | grep v4l2
如果出现libv4l2: error getting pixformat: Invalid argument
or:
v4l2loopback: module verification failed: signature and/or required key missing – tainting kernel
美观它。
4、建立媒体源
the simpest is:
$ gst-launch v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! v4l2sink device=/dev/video1
4.1、接收流媒体是:
$ gst-launch-0.10 udpsrc port=1234 ! theoradec ! ffmpegcolorspace ! ximagesink
发送流媒体是:
$ gst-launch-0.10 v4l2src ! ffmpegcolorspace ! theoraenc ! udpsink host=127.0.0.1 port=1234
注意先执行接收的。
4.2、显示或保存
显示视频:
$ gst-launch v4l2src ! xvimagesink
视频保存成文件:
$ gst-launch v4l2src ! video/x-raw-yuv,width=320,height=240 ! ffmpegcolorspace ! jpegenc ! avimux ! filesink location=osug-1.avi
4.3、某段音频伪装成相机video1:
$ gst-launch videotestsrc ! v4l2sink device=/dev/video1
查看下,ok:
$ cheese –device=/dev/video1
相机0伪装成相机1:
$ gst-launch v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! v4l2sink device=/dev/video1
查看下,ok:
$ cheese –device=/dev/video1
文件伪装成相机1:
$ gst-launch filesrc location=”/home/zdh991/tmp/osug-1.avi” ! avidemux ! v4l2sink device=/dev/video1
查看下,ok:
$ cheese –device=/dev/video1
IP相机伪装成相机1:
$ gst-launch souphttpsrc location=http://192.168.1.126:80 ! jpegdec ! ffmpegcolorspace ! v4l2sink device=/dev/video1
查看下,ok:
$ cheese –device=/dev/video1
5、利用iphone模拟测试
IP camera, gstreamer, and virtual video devices.
如果没有IP-camera,可以使用iphone的摄像头。
安装一个app例如third eye,让iphone接入局域网分配。
在iphone获取到ip地址后,从pc上测试通过浏览器输入iphone-ipaddress:8091,如果可以实时显示iphone摄像头的视频,说明okay。
利用gat-launch操作iphone的这个ip:port把这个摄像头作为wifi的ip-camera来使用:
$ gst-launch souphttpsrc location=”http://172.20.10.11:8091″ ! jpegdec ! ffmpegcolorspace ! v4l2sink device=/dev/video1
这里面172.20.10.11:8091就是IP-camera的地址和端口。注意pc和iphone在同一subnet。
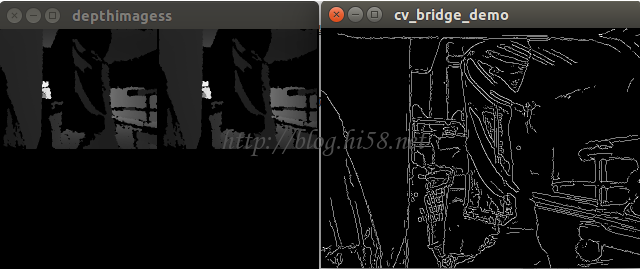
ros提供gscam这个node,可以用image view查看,例如:
$ gst-launch souphttpsrc location=http://[user]:[password]@[camera_ip]/mjpg/video.mjpg ! jpegdec ! v4l2sink device=/dev/video0
$ GSCAM_CONFIG=”rtspsrc location=rtsp://CameraIP/ipcam.sdp ! video/x-raw-rgb,framerate=30/1 ! ffmpegcolorspace”
$ rosrun image_view image_view image:=/gscam/image_raw
使用gscam也可以配合rosbridge的websocket,例如wss://ip:port。
这个工具只能建立简单地pipeline。尤其是它只在特定层级之上模拟pipeline和应用的交互。可以很简单的快速测试pipeline。注意gst-launch主要是一个调试工具,真正用gst_parse_launch()这个API来创建pipeline。
gst-launch的命令行包括一个在PIPELINE-DESCRIPTION之后的一系列选项。简单说,一个PIPELINE-DESCRPTION是一系列用!分隔开的元素:
$ gst-launch-0.10 videotestsrc ! ffmpegcolorspace ! autovideosink
这用videotestsrc,ffmpegcolorspace和autovideosink三个element。GStreamer会把他们的输出pad和输入pad连接起来,如果存在超过1个可用的输入/输出pad,那么就用pad的Caps来确定兼容的pad。
element
element可能是有属性的,在命令行里格式就是“属性=值”,多个属性用空格来分开。可以用gst-inspect工具来查一下element的属性。
$ gst-launch-0.10 videotestsrc pattern=11 ! ffmpegcolorspace ! autovideosink
element可以用name这个属性来设置名称,这样一些复杂的包含分支的pipeline可以创建了。有了名字,就可以使用前面创建的element,这在使用有多个pad的element(比如demuxer或者tee等)时是必不可少的。
$ gst-launch-0.10 videotestsrc ! ffmpegcolorspace ! tee name=t ! queue ! autovideosink t. ! queue ! autovideosink
这把videotestsrc先连接了ffmpegcolorspace,然后连接了tee element 这个tee就被命名成‘t’,然后一路输出到queue以及autovideosink,另一路输出到另一个queue和autovideosink。
Pads
在连接两个element时与其让GStreamer来选择哪个Pad,宁可直接指定Pad。可以在命名element后使用.+pad名字的方法来做到这点(element必须先命名)。同样可以用gst-inspect来查看element里面pad的名字。
$ gst-launch-0.10.exe souphttpsrc location=http://docs.gstreamer.com/media/sintel_trailer-480p.webm ! matroskademux name=d d.video_00 ! matroskamux ! filesink location=sintel_video.mkv
这使用souphttpsrc在internet上锁定了一个媒体文件,这个文件是webm格式的。可以用matroskademux来打开这个文件,因为媒体包含音频和视频,所以创建了两个输出Pad,名字分别是video_00和audio_00。把video_00和matroskamux element连接起来,把视频流重新打包,最后连接到filesink,这样就把流存到了一个名叫intel_video.mkv的文件。总之找了一个webm文件,去掉了声音,仅把视频拿出来存成了一个新文件。如果保持声音,那么就应该这样:
$ gst-launch-0.10.exe souphttpsrc location=http://docs.gstreamer.com/media/sintel_trailer-480p.webm ! matroskademux name=d d.audio_00 ! vorbisparse ! matroskamux ! filesink location=sintel_audio.mka
这里的vorbisparse element会从流里面取出一些信息,然后放到Pad的Caps里面,这样下一个element,也就是matroskamux就可以知道如何处理这个流了。这个处理在抓取视频的时候是不用做的,因为matroskademux已经做了这件事情。
注意上面两个例子中媒体没有被解码和播放,仅仅只是把数据搬动了一下而已。
Caps过滤
当一个element有不止一个pad时,连接下一个element可能是模糊不清的,因为下游的element可能有不止一个的兼容的输入pad,或者它的输入pad可以和所有的输出pad兼容。在这样的情况下,GStreamer会使用第一个可以连接的Pad,这样相当于说GStreamer是随机找一个pad来连接的。
$ gst-launch-0.10 souphttpsrc location=http://docs.gstreamer.com/media/sintel_trailer-480p.webm ! matroskademux ! filesink location=test
这里和上一个例用了同样的媒体文件和demuxer。finksink输入pad是任意格式,这意味着它可以接受所有的媒体格式。那么matroskademux的哪个pad可以接到filesink呢?video_00还是audio_00?无法知道。为了消除这种不确定性,前面例子中用了pad的名字的方法,这里使用Caps过滤的方法:
$ gst-launch-0.10 souphttpsrc location=http://docs.gstreamer.com/media/sintel_trailer-480p.webm ! matroskademux ! video/x-vp8 ! matroskamux ! filesink location=sintel_video.mkv
一个Caps过滤动作类似于让element不做任何动作,仅仅接受给出的Caps。在这个例子中,在matroskademux和matroskamux中间加入了一个ievideo/x-vp8的Caps过滤,这样就表明在matroskademux中我们仅仅需要能生成这种类型视频的输出Pad。
需要用gst-inspect工具来查看一个element能接受和生成的Caps,用gst-discoverer来查看文件里面包含的Caps。如果需要查看在pipeline里面一个element生成的Caps,在gst-launch里面使用-v参数即可。
一个调整视频比例的pipeline。videoscale element可以调整输入尺寸然后再输出。例子里面用Caps过滤设置了视频大小为320×200:
$ gst-launch-0.10 uridecodebin uri=http://docs.gstreamer.com/media/sintel_trailer-480p.webm ! queue ! videoscale ! video/x-raw-yuv,width=320,height=200 ! ffmpegcolorspace ! autovideosink